How can manufacturers ensure production efficiency and competitiveness? One of the effective solutions is embracing digital transformation — the implementation of innovative technologies into every manufacturing aspect helps production companies enhance their capabilities, shorten products’ time to market, and satisfy customers’ demands.
What are the other benefits of digital transformation for manufacturing? What are the applications of cutting-edge technologies in manufacturing? And what are real-world digital transformation examples? Read the article to find the answers.
Key Takeaways:
- Digital transformation in manufacturing involves the application of digital technologies to manufacturing processes.
- Manufacturing digitalization optimizes processes, increases efficiency, optimizes resources and costs, reduces waste, helps achieve sustainability.
- New technology in manufacturing include AI and automation, digital twin, Internet of Things, additive manufacturing, augmented reality.
- The most common challenges of manufacturing digital transformation are high costs, a lack of skilled resources, resistance to change, and data security.
What Is Digital Transformation In Manufacturing?
Digital transformation in the manufacturing industry refers to the application of digital technologies to any manufacturing process with the aim of its optimization, increasing the quality of the output, and enhancing overall efficiency. Like in other industries, digital transformation in manufacturing sector involves leveraging such technologies as artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML), the Internet of Things (IoT), additive manufacturing, augmented and virtual reality (AR/VR), etc. Integrating these advanced technologies makes it possible to create a smart and interconnected manufacturing environment which increases the efficiency of the manufacturing processes. Let’s explore the importance of manufacturing digital transformation in more detail.
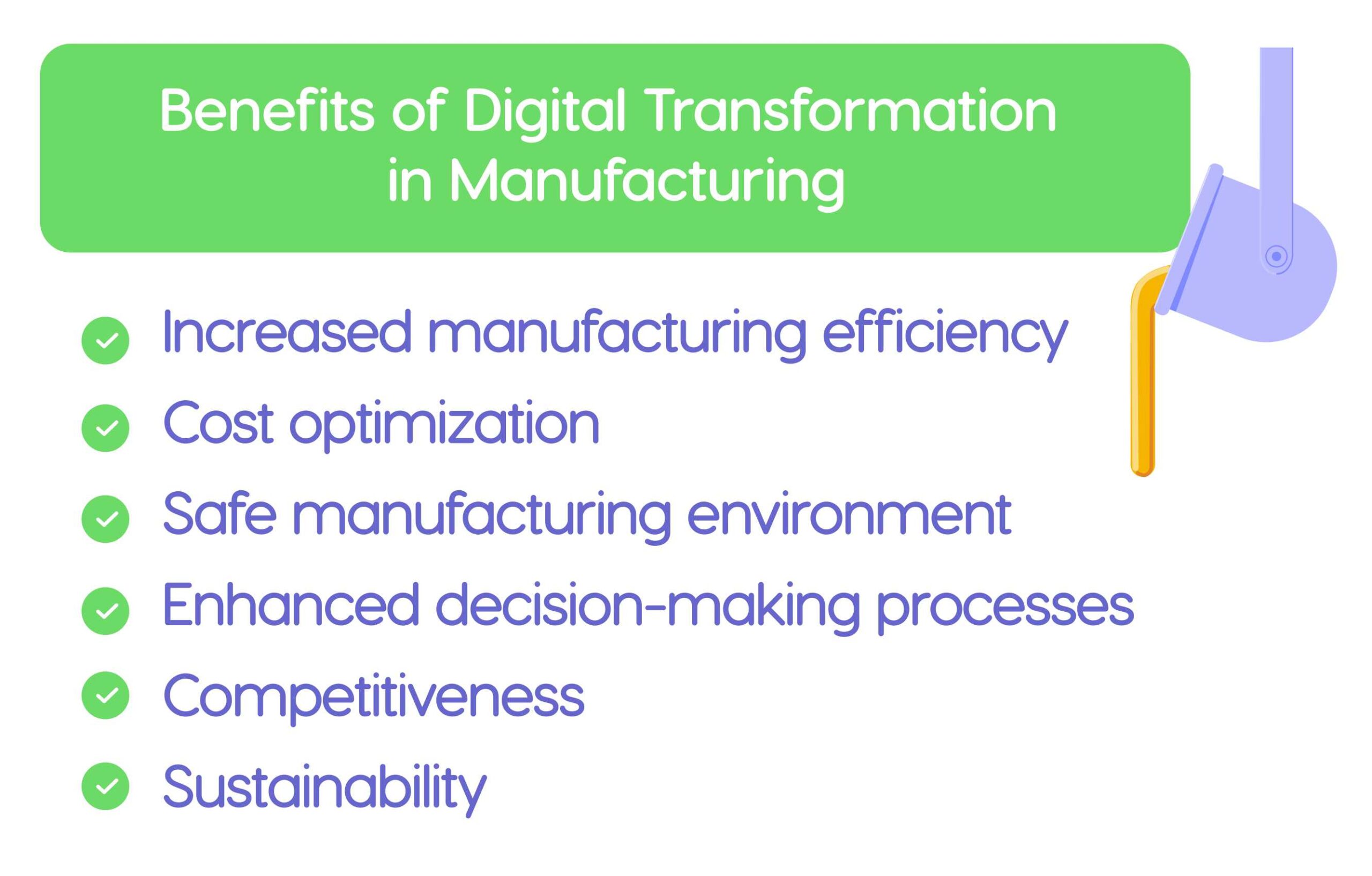
Benefits of Digital Transformation in Manufacturing
Implementing digital transformation for manufacturing companies allows them to improve current systems and processes, increase return on investment, and achieve business growth . Here are the benefits of digital business transformation manufacturing in more detail.
Increased manufacturing efficiency
Smart manufacturing eliminates the possibility of human errors that require rework and extra time. Also, it allows for delivering more output per unit of time. For example, additive manufacturing reduces time and costs for prototyping, which helps create the developed product faster. All these factors promote higher efficiency of the production process, more reasonable utilization of resources, and an increase in productivity.
Read more: Effective Manufacturing Operations Management in 2025
Cost optimization
Despite the high cost of digital investments, they will contribute to cost savings in the long run. Thanks to reducing waste and inefficiencies, increased productivity, more efficient resource utilization, effective risk forecasting and management, and making informed decisions, manufacturing companies reduce extra expenditures and increase profitability.
Safe manufacturing environment
Manufacturing industry digital transformation takes the safety of daily operations in the manufacturing environment to a new level. Forecasting, real-time monitoring, immersive training, and automation help manufacturers prevent accidents, minimize human errors, and ensure compliance with safety regulations. For example, artificial intelligence helps predict potential risks on the factory floor by analyzing historical and real-time data. AR and VR contribute to more effective personnel training. IoT and sensors monitor the state of the manufacturing equipment, environmental conditions, the state of workers’ health, which helps timely detect anomalies and prevent their negative impact.
Read more: Managing Risks in Manufacturing Projects: Essentials and Best Practices
Enhanced decision-making processes
Active use of big data and manufacturing analytics helps manufacturing companies get real-time actionable insights into the state of manufacturing processes and equipment performance. Also, they can use modeling and simulations to forecast the changes in the manufacturing plants, equipment failure, and other things. As a result, manufacturers can make more accurate and effective strategic decisions and take corrective actions when required.
Competitiveness
Following a digital transformation roadmap allows manufacturers to create products that meet customers’ needs to the full. For example, providing aftermarket services, which is one of the top digital transformation trends in manufacturing facilitated by technology integration, helps manufacturing companies increase customer loyalty. In addition, an increase in productivity and high quality of the developed product provide them with a competitive advantage.
Sustainability
Digital transformation promotes manufacturing with reduced environmental impact. The technologies like AI, the Internet of Things and sensors, real-time data analytics, etc. are effective solutions that help manufacturing companies optimize energy consumption, minimize waste, use their resources more reasonably, and reduce environmental footprint, which in turn contributes to compliance with sustainability regulations.
Now that the importance of digital transformation in manufacturing industry is clear, let’s take a closer look at the digital capabilities that enable it.
Manufacturing and Digital Transformation: Trends, Technology Applications and Examples
1. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning.
These digital solutions are one of the key drivers of digital transformation in manufacturing. They provide the following benefits to manufacturers.
Predictive maintenance
AI and ML algorithms along with predictive analytics are used to predict equipment failure: they analyze massive amounts of data from sensors incorporated in machines and use these insights to predict when maintenance is required. AI-powered predictive maintenance solutions help manufacturers reduce downtime, minimize maintenance costs, and optimize equipment utilization.
Quality control
AI is used in quality control systems; they leverage computer vision to examine imperfections in the manufactured products. These AI-powered systems help identify defects that may remain unnoticed by human inspectors, which contributes to higher product quality.
Demand forecasting
With AI and ML, manufacturers can forecast the demand for products more accurately, which contributes to more effective production and planning inventory management.
Aftermarket services
Digital transformation helps manufacturers take a proactive and data-driven approach to providing aftermarket services, which are becoming a source of revenue and profit for manufacturing companies. Deloitte states that in 2026, they are going to increasingly rely on agentic AI to increase the quality of services provided.
Examples
BMW automotive manufacturer utilizes AI-driven technology Car2X that enables real-time interaction between the vehicle and the BMW production system during the manufacturing process. In addition, its AIQX technology helps detect issues in the assembly process thanks to cameras and sensors in the conveyor belt process. [1]
Also, in recent years, manufacturing companies tend to leverage Generative AI. For example, Bosch has launched GenAI pilot projects that are expected to minimize the time required for rolling out and setting up AI solutions at their plants. [2] PepsiCo uses generative AI to test new design options and improve its products. In particular, the technology allowed them to improve the shape and flavor of their Cheetos. At first, they taught the machine the formula of ideal products, then generative AI could suggest further improvements to the product. [1]
2. Digital Twin.
A digital twin is a virtual replica of a physical object or a process, which helps simulate real situations and their outcomes. The technology can be used for predictive maintenance: it simulates the behavior of equipment under various conditions, which helps identify potential issues before they turn into serious problems and facilitates equipment performance improvement.
Example
Rolls Royce creates digital twins of aircraft engines they produce. Digital twins simulate engine performance under various conditions, which helps the manufacturers understand how it can perform in different situations. These insights are valuable, as it’s nearly impossible to conduct these tests in real-life circumstances. In addition, the technology helps manufacturers forecast when the engines will require maintenance. [3]
3. Internet of Things (IoT).
IoT in manufacturing can be used for the following purposes.
Smart manufacturing technology
IoT devices get real-time data from production lines, which provides manufacturers with granular visibility into equipment performance, operational efficiency, and energy usage. This allows them to take data-driven actions and timely address issues if any.
Supply chain optimization
A wide range of sensors provide visibility into inventory levels, shipment status, and environmental conditions, which helps track materials or products throughout the supply chain and ensure timely delivery.
Example
Siemens’ InsightsHub platform connects machines and systems with the aim of optimizing complex processes on the factory floor. The platform uses the Industrial Internet of Things technology to gain insights required to accelerate production processes, make them more adaptive, and people-centric. [4]
4. Automation.
Automation in manufacturing is one of the most essential drivers of increasing efficiency. Manufacturers can automate dangerous, time-consuming, and repetitive tasks (welding, painting, assembly, packaging, and other human activities) by using industrial robots. They can perform these tasks with high precision and speed, which is especially relevant for industries with high volumes of production and strict quality standards.
Example
At Tesla’s Gigafactory in Shanghai (China), 95% of operations are automated, which has allowed the company to reach a cycle time of less than 40 seconds. Increased use of automation enabled them to produce a million cars within just a year compared to 2.5 years required for producing their first million vehicles. Therefore, automation helps Tesla meet the growing demand for cars with unprecedented efficiency. [5]
5. Additive Manufacturing technologies (3D Printing).
Additive manufacturing involves creating 3D objects layer-by-layer. It’s widely used in manufacturing, especially in industries that require creating complex products like in aerospace and defense or automotive. What are the advantages of this technology? It allows for creating product prototypes quickly and with less cost, which optimizes their design and reduces their time-to-market. It also helps create necessary parts for maintenance and repair purposes; the technology enables creating them wherever it’s needed.
Example
Boeing has begun testing 3D printing of the whole main rotor system of the Apache attack helicopter. 3D printing the parts will allow the company to reduce lead times and minimize the dependence on supply chain disruptions. [6]
6. Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR).
The immersive technologies can be used in the following areas.
Training
Immersive technologies (augmented and virtual reality) allow manufacturing workers to learn in a controlled environment, which optimizes their readiness to work in high-risk manufacturing sites, operate complex equipment, or handle emergency situations.
Equipment maintenance and repair
Manufacturing technicians can use AR applications to perform complex maintenance and repair tasks. This minimizes human errors and accelerates the repair process.
Examples
Ford manufacturing teams use augmented and virtual reality to collaborate and exchange experiences regarding training or assembly techniques. For example, AR allows engineers to visualize design flaws or streamline the assembly process, while VR is widely used for training in a safe environment. These technologies not only help technicians tackle their issues but also optimize the company’s manufacturing workstations in different corners of the world. [7]
At Airbus, operators wear augmented reality glasses when performing complicated tasks. For example, it helps them work with heavy parts and keep all the required information about them. Also, this increases safety of the workplace. Successful applications of the technology will contribute to its more diverse use by the company. [9]
7. Big Data and Analytics.
Manufacturers use big data and analytics to optimize their processes. Data analytics helps identify patterns and trends, which contributes to improving efficiency and minimizing waste of materials and efforts. Big data analytics facilitate production and tool optimization, predictive maintenance and quality control, employee safety, better supply chain management, and continuous improvements. In addition, manufacturers can analyze customer data to understand their preferences and create products that meet their needs. In turn, this can increase customer satisfaction and increase sales.
Example
Honeywell has introduced a software digitalization solution Honeywell Batch Historian that provides manufacturers with historical data for reporting and analytics. The solution will increase the efficiency of data analysis and contribute to more effective automation of the company’s production processes. [8]
Now that you understand what technologies enable digital transformation in manufacturing, we can take a quick look at recent trends that will impact the process of digitizing manufacturing.
Other Digital Transformation Trends in Manufacturing
Digital transformation in manufacturing isn’t limited to the above-mentioned technlologies. Let’s see how advanced technologies change the game for manufacturers.
- Cybersecurity: This trend is explained by increased connectivity of digital systems used by manufacturers and their vulnerability to cyber risks.
- Green manufacturing: With the help of digital ecosystems, manufacturers can achieve energy efficiency, reduce waste and emissions.
- Data-driven decision-making: Using data and analytics helps manufacturers make more effective decisions when it comes to demand forecasting, addressing risks, and optimizing manufacturing and supply chain processes.
- Supply chain digitalization: Achieving supply chain visibility and AI-powered simulations and forecasting helps manufacturers achieve supply chain resilience.
- Integration of project and portfolio management tools: Leveraging PM and PPM tools for conducting digital transformation initiatives streamlines DT processes, helps utilize resources effectively and achieve desired outcomes.
In 2026, technology trends in manufacturing won’t change fundamentally, they are here to stay for years ahead. According to Deloitte Manufacturing Outlook for 2026, companies will continue investing in smart manufacturing and operations. This will include automation hardware, data analytics, sensors, and cloud computing.
In a great number of cases, digital transformation in manufacturing doesn’t come down to real-world success stories; it often doesn’t run smoothly, and companies face challenges on the way to its implementation. Let’s take a quick look at possible issues you may come across.
5 Challenges of Digital Transformation in Manufacturing
1. High costs.
Implementing digital transformation in manufacturing companies is costly. New technologies require considerable investments in new equipment and required software. In addition, leveraging technologies requires tech-savvy employees, which is also costly.
2. Resistance to change.
This is the most common obstacle in implementing digital transformation, and manufacturing industry is no exception. “We’ve always done it this way” is a motto of employees who withstand transformations. In addition, people with this mentality may find it difficult to learn how to work with latest digital solutions, which makes DT implementation even more difficult.
3. A lack of digital workforce.
Tech-savvy employees are in great demand across industries now. This causes shortages of skilled professionals who can work with digital technologies and hampers DT implementation in manufacturing companies.
4. Data security.
Increased connectivity intensifies data security risks and makes digital systems and equipment vulnerable to cyber attacks. Ensuring data security requires additional effort and costs.
5. Disruption in manufacturing workflows.
Implementing changes and digital technologies can temporarily hamper existing manufacturing operations and production schedules. This happens because digital technologies may not work as expected at once, and current employees require time to get a handle on them.
Transform Manufacturing Industry with Epicflow
One of the components of successful digital transformation in manufacturing is leveraging digital tools to optimize managing manufacturing projects and resources. Epicflow manufacturing resource management tool facilitates the effective orchestration of parallel manufacturing projects and wise management of their shared resources. Companies choosing Epicflow achieve the following results:
- Efficient utilization of resources across multiple projects;
- Ensuring the seamless flow of large and complex projects;
- Optimizing portfolio based on the business value and resource constraints;
- Having visibility into essential project and resource data across the whole project environment;
- Reducing project lead times;
- Delivering more value with resources available;
- Making data-driven decisions;
- Dealing with uncertainty and managing risks effectively.
Contact our experts to learn more about how Epicflow transforms digital transformation manufacturing projects and how it facilitates project success under conditions of uncertainty and change.
Final Words
As we see, the impact of technology on manufacturing is huge. The digital transformation process is disrupting the manufacturing industry — it dramatically changes the way manufacturing processes are executed and opens up new opportunities for manufacturers. Digital transformation efforts involving the application of AI and ML, automation, IoT, sensors, 3D printing, and other innovative technologies and tools (e.g., manufacturing scheduling software) that allow manufacturers to increase the efficiency of production operations, reduce costs, optimize resource allocations, achieve greater flexibility, and stay competitive in the rapidly changing manufacturing landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is digital transformation in the manufacturing industry?
Digital transformation in manufacturing is the application of digital technologies in all manufacturing processes, from producing things to supply chain management. The manufacturing technologies examples include AI, IoT, data analytics, automation, etc.
What are the key benefits of digital transformation in manufacturing?
The most essential benefits of digital transformation of manufacturing include increased efficiency, improved quality of the manufactured products, optimization of production costs, enhanced flexibility, improved decision-making processes, enhanced customer experience, promoting a culture of innovation, sustainability, and competitive advantage.
What are the factors affecting the digital transformation journey in manufacturing companies?
The success of digital manufacturing transformation initiatives depends on investment in digital technologies, the existing infrastructure, digital workforce availability, an organization’s readiness for change, and the effectiveness of the change management process.
What are the key technologies that enable digital transformation in manufacturing?
The following technologies enable digital transformation in manufacturing: artificial intelligence, machine learning, the Internet of Things, sensors, automation, 3D printing, augmented and virtual reality (AR/VR), and digital twin.
How is digital technology used in manufacturing?
AI and ML are used for demand forecasting, predictive maintenance, and quality control. Digital twins are used for simulations and more effective decision-making. The Internet of Things helps assess equipment performance, operational efficiency, and energy consumption. With 3D printing, manufacturers can create required objects quicker and at a lower cost (e.g., spare parts for the automotive or aerospace industry). Immersive technologies are used for training personnel and equipment maintenance.
What is an example of digitalization in manufacturing?
An example of digitalization in manufacturing industry is the use of digital twin technology. This is a digital replica of a product or a process, which is used by manufacturers to monitor, run simulations, identify bottlenecks, and use these insights to improve processes.
References
- AI in Product Development: Netflix, BMW, and PepsiCo. Retrieved from: https://www.virtasant.com/ai-today/ai-in-product-development-netflix-bmw#:~:text=BMW’s%20Car2X%20technology%20enables%20real,using%20sensor%20technology%20and%20AI.
- Bosch to Use Generative AI in Manufacturing. (2024). Retrieved from: https://www.boschmediaservice.hu/en/press_release/bosch_artificialintelligence_manifacturing_2024-391.html.
- How Digital Twin Technology Can Enhance Aviation. Retrieved from: https://www.rolls-royce.com/media/our-stories/discover/2019/how-digital-twin-technology-can-enhance-aviation.aspx.
- Siemens PLM Software. Insights Hub. Retrieved from: https://plm.sw.siemens.com/en-US/insights-hub/.
- Tesla Manufacturing Post. Retrieved from: https://x.com/gigafactories/status/1743312868899008954.
- Boeing Begins 3D-Printing Apache Helicopter Parts (2023). https://www.defensenews.com/industry/techwatch/2023/10/18/boeing-begins-3d-printing-apache-helicopter-parts/.
- Ford Motor Enters Digital Era With Its Advanced Manufacturing Center. Retrieved from: https://connectedmanufacturing.wbresearch.com/blog/ford-motor-company-advanced-manufacturing-center-strategy#:~:text=With%20internet%20connectivity%2C%20the%20design,sharing%20the%20same%20virtual%20experience
- Honeywell Introduces Batch Historian To Digitalize Manufacturing Operations. Retrieved from: https://automation.honeywell.com/us/en/news/press-releases/2024/honeywell-introduces-batch-historian-to-digitalize-manufacturing-operations.
- Mixed Reality to Meet Future Challenges. Retrieved from: https://www.airbus.com/en/newsroom/stories/2023-06-mixed-reality-to-meet-future-challenges#:~:text=In%20manufacturing%2C%20augmented%20reality%20glasses,right%20in%20front%20of%20them.