There is no doubt now that Agile is not just a buzzword, but a really working methodology that takes product development to the next level.
Starting as an approach to improving the software development process, Agile has gone far beyond that and evolved into a kind of philosophy or mindset that can transform processes not just in product development, but in the whole organization.
So, what makes it so special? How does it differ from the traditional approach to product development? Are there any disadvantages of the Agile methodology? Read further to find out the answers.
What is Agile Product Development?
Agile methodology was initially created for the software development teams dealing with changing requirements and uncertainty, but over time, it has transformed into a mindset that helps organizations run their processes under conditions of change and uncertainty. Also, it has gone beyond software development and become applicable to any product creation process.
We can define Agile product development as a dynamic, flexible, and iterative approach to creating products that is focused on iterative progress, collaboration with customers and meeting their needs, and adaptability. Agile product development aims to deliver value to customers more frequently and effectively through iterative and incremental progress. In this way, agile methodology helps respond to changes quickly and efficiently, which contributes to higher-quality products and increased customer satisfaction.
The Agile approach to product development is based on 12 specific principles. Initially, they were generated for software products, but most of them are also suitable for any product development. Let’s take a quick look at these principles.
Principles of Agile Product Development
1. Customer satisfaction.
Agile prioritizes customer satisfaction, which is achieved through regular value delivery and creating customer-centric products.
2. Welcoming change.
Agile supports changing requirements at any stage of the project lifecycle. It regards changes as opportunities to ensure customer satisfaction and gain a competitive advantage.
3. Frequent delivery.
Agile aims to shorten the time between planning and value delivery by reducing pre-work documentation. Delivering software features every few weeks to months is ideal.
4. Close collaboration of business people and developers.
Daily collaboration between business people and the Agile development team keeps the management engaged, helps promptly address issues, enhances the efficiency of work and the quality of the developed product.
5. Empowering and supporting teams.
An agile product development environment makes teams motivated, trusted, empowered to make decisions and perform their work without micromanagement. This increases agile teams’ engagement and improves product development results.
6. Effective communication.
It aims to reduce uncertainty and strengthen collaboration between all those involved in product development. This recommendation is particularly relevant in the present-day hybrid and remote work environment.
7. Measured progress.
A working product (initially software) that meets customers’ expectations and needs is the primary measure of progress.
8. Sustainable development.
This involves keeping a constant pace of product delivery – the development team working on Agile projects should be productive but at the same time, they shouldn’t be overwhelmed with the amount of work assigned to them.
9. Technical excellence.
The delivered product should be of the highest possible quality and well-designed.
10. Simplicity.
This principle emphasizes avoiding unnecessary actions. If you can do something in a simple way and with less effort, don’t make it complicated. This saves team members’ effort and time they can spend on things that are essential to product success.
11. Self-organizing teams.
This recommendation highlights the crucial role of teams that are fully responsible for allocating tasks, tracking progress, and are empowered to make decisions. The members of these self-organizing teams are more motivated, which is an essential prerequisite for fruitful work on product development.
12. Regular reflection.
Finally, Agile teams should constantly review their performance, detect inefficiencies, and adjust their work accordingly. This will help the team members enhance their efficiency.
As we see, these core principles are focused on delivering continuous value to customers and creating an adaptive and collaborative environment for the development team.
Overview of Traditional SDLC vs Agile Approach
Basically, Agile methods have appeared as an alternative to the traditional methodology of software development, so let’s outline the main characteristics of these approaches and how they differ from each other.
SDLC (software development life cycle) is a sequential approach to software development. It can be represented as a series of the following phases: planning, design, development, testing, implementation, and maintenance of a product. The main idea behind this approach is that the output of one phase becomes the input for the next one. This makes it similar to the Waterfall approach to project management.
The traditional development cycle has a clear structure of the whole development process, unchanged requirements, detailed documentation; requires careful planning, and is generally easy to manage.
However, this methodology has certain limitations that can make product development less efficient, e.g.:
- longer time for product delivery: the testing phase comes late in SDLC, which can cause serious delays in case there are some mistakes made at the beginning that require rework,
- lack of flexibility: customers can change their minds regarding the initial requirements of a product, but the methodology doesn’t allow changes to be made,
- limited customer involvement: there is no opportunity to receive their constant feedback as to the product’s functionality.
As an approach to product development, Agile can be defined as a set of practices used by dev teams to deliver more user-centric products. It allows companies to deliver output under conditions of frequent change and uncertainty so that they can easily adapt to them when necessary.
In contrast to SDLC, Agile product development methodology involves iterative planning and testing and accepts changing requirements, which makes it possible to deliver a product that meets customers’ needs to the full. This is achieved thanks to the Agile principles listed above and the values established in the Agile Manifesto.
There are several Agile practices: Scrum, Kanban, Scrumban, Lean, XP, and more. Each of them has certain peculiarities, so development teams can choose the one that works best for them.
One more distinctive features of Agile framework is its focus on collaboration and self-organizing cross-functional teams. That doesn’t mean that Agile product development teams don’t need a manager, but that they have more freedom in making certain decisions.
So, the main difference between Agile processes and traditional development is that SDLC is a sequential process, while Agile is iterative. The table below presents their distinctions in more detail.
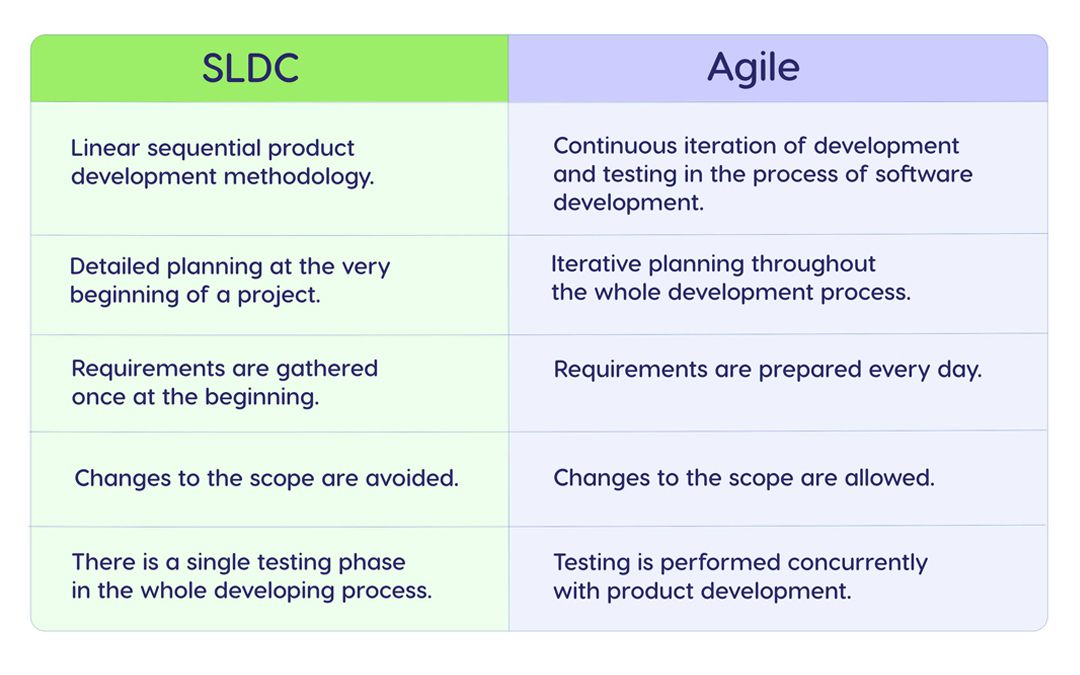
Consequently, the Agile approach makes it possible to create a product in close interaction with customers and improve it simultaneously with the development process.
Read more: The Scrum Framework: Advantages, Disadvantages and Ways of Handling Possible Issues
Now, let’s take a closer look at the Agile product development process itself.
Agile Product Development Model: Essential Steps
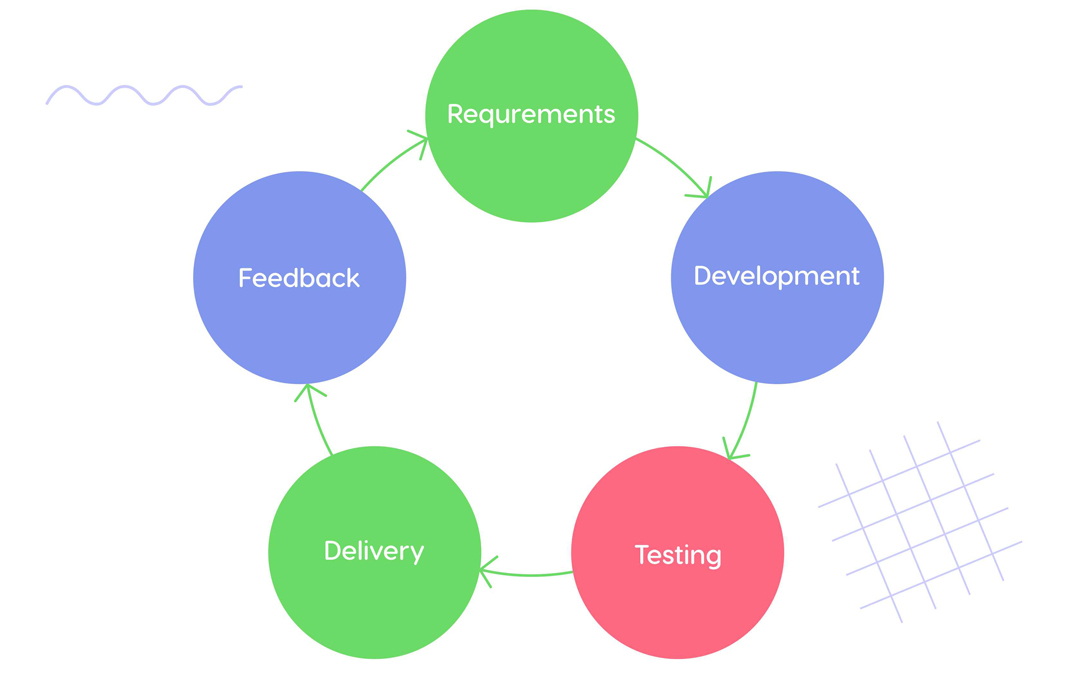
The Agile product development process is based on iterations – standard time frames during which Agile teams deliver certain value. They usually last from 1 to 4 weeks. The very first iteration aims to deliver a product with basic functionality, and the rest of the features will be added during the next iterations.
The iterative development process consists of the following phases.
Concept and initiation
First and foremost, the Agile product team defines an overall product vision and its objectives, target audience, and a product’s key features. At this phase, it’s essential to engage stakeholders to gather their requirements, needs, and expectations. After that, the team creates a product backlog that covers all features, bug fixes, and enhancements required for the product.
Sprint planning
At the planning stage, the created project backlog should be broken down into sprints lasting for 1-4 weeks. Each sprint has its goal that determines which items from the backlog will be completed during the sprint. Then, the backlog items are further divided into tasks that are assigned to the product development team members.
Design and prototyping
At this stage, the software developers create user stories and use cases to show how the developed product will be used. Designers create mockups and prototypes that will visualize the developed product and its features.
Development
This stage involves the development process itself. As for software development, the team should also integrate the developed code into a shared repository, allowing them to detect and fix problems.
Testing
This development phase embraces unit testing (testing individual components), integration testing (making sure that various elements work together properly), acceptance testing (validating the developed product based on user stories), and bug fixing (fixing problems identified during the testing phase).
Review and retrospective
Each sprint finishes with a sprint review which presents the accomplished work to stakeholders with the aim of gathering their feedback. Also, the sprint retrospective is performed: it shows what went well, what was inefficient, and how the team can improve things in the next sprint.
Deployment
Finally, the team can plan the release of the product (or its part) and deploy it to the production environment.
Maintenance and support
As soon as the product is released, the development team should regularly monitor its performance and fix any issues/bugs that arise. It’s also essential to support users and gather customer feedback that will be the basis for further improvements.
Iteration and continuous improvement
User experience and customer feedback should be used to update the backlog with new features and changes.
These iterations will be repeated again and again until all the requirements are met and the final product can be delivered to customers.
Now that the essence of the Agile framework for product development is clear, let’s analyze its advantages and drawbacks.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Agile Product Development

The popularity of the Agile methodology and its expansion to business processes speak for themselves: under the right circumstances, it has proved its effectiveness. At the same time, the Agile methodology is not a silver bullet, and as any other methodology has certain drawbacks.
Let’s review the advantages and limitations of this methodology in more detail.
The advantages of Agile in product development
-
Focus on users and business value.
The features added to the product are based on real users’ needs and their feedback obtained during each iteration. Similarly, this contributes to satisfying customers’ business needs as well as higher customer satisfaction.
-
Early delivery.
Working in constant iterations (or sprints as their variants) allows the team to deliver certain features to customers regularly.
-
Better quality of a product.
Frequent testing and reviews as well as breaking down the whole development process into smaller parts make it possible to improve the quality of a product being developed.
-
Flexibility.
The present-day business environment is surrounded by uncertainty and changes, therefore customer behavior and requirements tend to change as well. With the flexible methodology, the development teams can deliver a product that corresponds to these changing conditions.
Disadvantages of Agile methodology in product development
At the same time, Agile is not a one-size-fits-all solution, and its effectiveness will be determined by certain circumstances. Below are some limitations of the methodology.
-
Lack of detailed documentation.
This may result in misinterpretations of the requirements to the product in development or even confusion among the team members. In addition, if new members join the team, it will be difficult for them to make sense of the work the rest of the team is doing.
-
Higher probability of scope creep.
As long as customers’ requirements often change, and the initial planning is not that detailed, it may be rather difficult to keep the development process on track and avoid scope creep.
-
Low predictability of the final outcome.
It can be difficult to assess the efforts and time required for certain deliverables. Changing requirements and lack of detailed planning add to poor predictability of the final outcomes. Also, as long as there is no strict schedule, finishing the development project on time may require additional effort.
It’s also important to note that the success of Agile product development depends on certain factors: team members’ capability and training, organization culture, communication between the participants, the effectiveness of project management, and more [1].
So it’s up to an organization to weigh all the pros and cons when choosing the best working software development methodology.
Frequently Asked Questions
As a conclusion, let’s give answers to the most popular questions about Agile methodology for product development.
1. What is Agile product development methodology?
Agile product development is a dynamic and adaptive approach to creating products, which emphasizes iterative progress, collaboration with customers, and adaptability. Its goal is to deliver value more frequently and effectively through continuous iterations and constant improvements.
2. Why is Agile good for product development?
The main advantages of the Agile development principles include the focus on users and their needs, continuous delivery, focus on the high quality of the delivered product, and flexibility.
3. What are the five steps in agile development?
Agile product development comes down to the following phases: identifying requirements, product development, testing, delivery, and feedback that will become the basis for the next iteration’s requirements.
Finally, no matter what methodology you choose, the product development process can be significantly improved with effective project/resource management software. Epicflow is a powerful and flexible multi-project resource management solution that allows you to manage multiple projects running concurrently and achieve better outcomes thanks to smart resource and task management functionality as well as predictive analytics capabilities. In addition, it has its own approach to managing tasks and projects, which works well with any product development or project management methodology. Сontact us if you’d like to learn more about our product.
References
Aldahmash, A., Gravell, Andy M., & Howard, Y. (2017). A Review on the Critical Success Factors of Agile Software Development. European Conference on Software Process Improvement. University of Southampton.